问题问题/漫画:http://xkcd.com/287/解决NP完全问题在XKCD
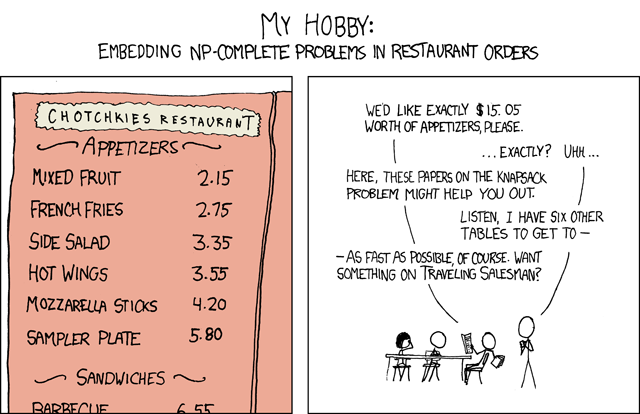
我不知道这是做的最好的方式,但这里是我想出什么迄今为止。我使用CFML,但它应该是任何人都可读的。
<cffunction name="testCombo" returntype="boolean">
<cfargument name="currentCombo" type="string" required="true" />
<cfargument name="currentTotal" type="numeric" required="true" />
<cfargument name="apps" type="array" required="true" />
<cfset var a = 0 />
<cfset var found = false />
<cfloop from="1" to="#arrayLen(arguments.apps)#" index="a">
<cfset arguments.currentCombo = listAppend(arguments.currentCombo, arguments.apps[a].name) />
<cfset arguments.currentTotal = arguments.currentTotal + arguments.apps[a].cost />
<cfif arguments.currentTotal eq 15.05>
<!--- print current combo --->
<cfoutput><strong>#arguments.currentCombo# = 15.05</strong></cfoutput><br />
<cfreturn true />
<cfelseif arguments.currentTotal gt 15.05>
<cfoutput>#arguments.currentCombo# > 15.05 (aborting)</cfoutput><br />
<cfreturn false />
<cfelse>
<!--- less than 15.05 --->
<cfoutput>#arguments.currentCombo# < 15.05 (traversing)</cfoutput><br />
<cfset found = testCombo(arguments.currentCombo, arguments.currentTotal, arguments.apps) />
</cfif>
</cfloop>
</cffunction>
<cfset mf = {name="Mixed Fruit", cost=2.15} />
<cfset ff = {name="French Fries", cost=2.75} />
<cfset ss = {name="side salad", cost=3.35} />
<cfset hw = {name="hot wings", cost=3.55} />
<cfset ms = {name="moz sticks", cost=4.20} />
<cfset sp = {name="sampler plate", cost=5.80} />
<cfset apps = [ mf, ff, ss, hw, ms, sp ] />
<cfloop from="1" to="6" index="b">
<cfoutput>#testCombo(apps[b].name, apps[b].cost, apps)#</cfoutput>
</cfloop>
上面的代码告诉我,增加了高达$ 15.05的唯一组合是杂果7项目,它需要我testCombo功能的232个执行完成。
有没有更好的算法来找到正确的解决方案?我有没有找到正确的解决方案?
美丽。你可能会被关闭,因为它不是一个问题:( – Meff 2008-09-26 20:36:04
你错过了1个采样器,2个热翅膀,1个混合水果 – Randy 2008-09-26 20:38:35
哎呀,不小心留下了我打算问的问题,我已经添加了。 ! – 2008-09-26 20:38:39